Understanding the ATM LANE (LAN Emulation)
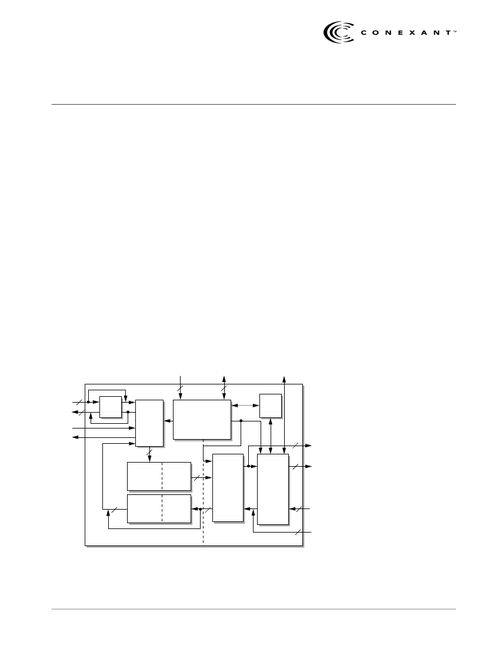
ATM LANE, or LAN Emulation, is a crucial technology that allows ATM networks to emulate traditional LAN technologies like Ethernet and Token Ring. This enables seamless integration of ATM networks with existing LAN infrastructures without the need for modifications to higher-level protocols. Let’s delve into the intricacies of ATM LANE and its significance in modern networking.
Components of ATM LANE
The ATM LANE architecture consists of several key components that work together to facilitate the emulation of LAN services over ATM networks. These components include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| LAN Emulation Configuration Server (LECS) | Manages the configuration of LANE clients and servers, including address allocation and virtual circuit setup. |
| LAN Emulation Server (LES) | Handles the emulation of LAN services, such as broadcast and multicast, and provides connectivity between LANE clients and servers. |
| Broadcast and Unknown Server (BUS) | Manages the distribution of broadcast and unknown unicast traffic within the ATM network. |
| LAN Emulation Client (LEC) | Represents the network devices that require access to the ATM network, such as PCs, printers, and servers. |
Protocol and Interactions
ATM LANE defines a set of protocols and interactions between LANE clients and servers. These protocols include:
-
Initial Setup: Establishing a connection between the LANE client and server.
-
Registration: Registering the LANE client with the LES and LECS.
-
Address Resolution: Resolving the MAC addresses of LANE clients.
-
Data Transmission: Sending and receiving data between LANE clients and servers.
Communication and Virtual Circuits
Communication between LANE clients and servers is facilitated through ATM Virtual Channel Connections (VCCs). These VCCs can be point-to-point or point-to-multipoint, depending on the type of traffic being transmitted.
-
Point-to-Point VCCs: Used for direct data, direct control, direct configuration, default multicast, and optional multicast traffic.
-
Point-to-Multipoint VCCs: Used for multicast forwarding and control.
Benefits of ATM LANE
ATM LANE offers several benefits, including:
-
Seamless Integration: Allows ATM networks to coexist with traditional LAN technologies without requiring modifications to existing network infrastructures.
-
Improved Performance: Provides better performance and reliability compared to traditional LAN technologies.
-
Scalability: Supports large-scale network deployments with high bandwidth and low latency.
Applications of ATM LANE
ATM LANE is widely used in various applications, such as:
-
Enterprise Networks: Facilitates the integration of ATM networks with existing LAN infrastructures in corporate environments.
-
Telecommunications: Enables the delivery of high-quality voice, video, and data services over ATM networks.
-
Financial Services: Provides secure and reliable connectivity for ATM machines and other financial devices.
Conclusion
ATM LANE is a vital technology that enables the seamless integration of ATM networks with traditional LAN technologies. By providing improved performance, scalability, and reliability, ATM LANE has become an essential component of modern networking infrastructures.
